明天组会讲Circuit PSI,事先预习一下前置知识
参考资料:
【知乎专栏】隐私集合求交(Private Set Intersection)问题综述
PSI
隐私求交(Private Set Intersection, PSI)可能是被研究最多的具体的多方安全计算(Secure Multiparty Computation, MPC)协议。PSI本质上是一种特殊的多方安全计算协议:计算双方各自有一个集合,要求双方协作共同计算出两者集合的交集,计算过程中(除了交集部分)不泄露任何和各自集合相关的信息。
标准的PSI分为几大类:基于密钥交换(Diffie-Hellman key exchange based)、基于透明传输 (oblivious transfer based, OT-based)、基于透明键-值(oblivious key-value stores based, OKVS-based)、基于透明向量线性估值(Vector Oblivious Linear Evaluation, VOLE-based)、基于多项式操作(polynomial manipulation)、基于分支程序(Branching Program, BP)。
除此之外还有隐私求交集基数(Private Intersection Cardinality)、阈值隐私求交(Threshold Private Set Intersection)、电路隐私求交(Circuit-PSI)、模糊隐私求交(Fuzzy-PSI)等变体。
电路隐私求交(Circuit-PSI)
Circuit-PSI 的开篇之作:Private set intersection: Are garbled circuits better than custom protocols?
Yao’s Garbled Circuits
Evan 和 Ginny 正在决定是否进行合作,我们希望如果其中一方不希望进行合作,那么他不会知道对方的态度。使用 Yao’s Garbled Circuits 可以实现这一点,其中 Ginny 扮演 garbled circuit generator(or garbler) 的角色,负责生成一个混淆 AND 门;Evan 扮演 evaluator 的角色,负责对 AND 门求值。
Ginny 生成四个随机串 \(W^0_G\), \(W^1_G\), \(W^0_E\), \(W^1_E\),表示双方的选择。用 \(g\) 和 \(e\)(它们的值为 \(0\) 或 \(1\)) 代表双方的选择,\(H(W^g_G,W^e_E)\) 生成一个对称加密密钥,用来加密 \(g\land e\) 的结果。混淆门包括四个乱序的密文,\(\text{Enc}(H(W^g_G,W^e_E),g\land e),g=0/1,e=0/1\)。
Evan 使用透明传输(Oblivious Transfer, OT),在不告知 Ginny \(e\) 的值的同时获取 \(W^e_E\)。同时 Ginny 将 \(W^g_G\) 发送给 Evan。然后 Evan 就可以根据 \(H(W^g_G,W^e_E)\) 解密结果了。
需要注意的一点是,Evan 需要知道解密是否成功,因此直接将密钥和结果XOR是不行的。
定义
A garbling scheme \(\mathcal G\) consists of four polynomial-time algorithms \((\text{Gb}, \text{En}, \text{Ev}, \text{De})\).
- \(\text{Gb}(1^{\lambda}, f)\to (F, e, d)\)
The garbling algorithm \(\text{Gb}\) takes in the security parameter and a circuit \(f\), and returns a garbled circuit \(F\), encoding information \(e\), and decoding information \(d\).- \(\text{En}(e, x)\to X\)
The encoding algorithm \(\text{En}\) takes in the encoding information \(e\) and an input \(x\), and returns a garbled input \(X\).- \(\text{Ev}(F, X)\to Y\)
The evaluation algorithm \(\text{Ev}\) takes in the garbled circuit \(F\) and the garbled input \(X\), and returns a garbled output \(Y\).- \(\text{De}(d, Y)\to y\)
The decoding algorithm \(\text{De}\) takes in the decoding information \(d\) and the garbled output \(Y\), and returns the plaintext output \(y\).A garbling scheme \(\mathcal G = (\text{Gb}, \text{En}, \text{Ev}, \text{De})\) is projective if \(e\) consists of a \(2n\) wire labels, where \(n\) is the number of input bits. We denote those wire labels as \((X_i^0, X_i^1)_{i\in\text{inindices}}\). \(\text{En}(e, x=(v_i)_{i\in\text{inindices}})\) then returns \(X=(X_i^{v_i})_{i\in\text{inindices}}\). Similarly, we call a garbling scheme output-projective if d consists of \(2\) labels for each output bit, one corresponding to each possible value of that bit.
正确性
A garbling scheme \((\text{Gb}, \text{En}, \text{Ev}, \text{De})\) is correct if for all sufficiently large security parameters \(\lambda\), for all functions \(f\) and inputs \(x\), \[\text{Pr}[(F, e, d)\leftarrow \text{Gb}(1^{\lambda}, f):\text{De}(d, \text{Ev}(F, \text{En}(e, x)))=f(x)] = 1\]
安全性
[BHR12] 定义了三个安全概念:obliviousness,privacy 和 authenticity。obliviousness 要求 \(F\) 和 \(X\) 不会暴露关于 \(x\) 的任何信息;privacy 要求通过 \(d\) 无法获取除 \(y\) 以外的关于 \(x\) 的任何信息;authenticity 要求无法用 \(F\) 和 \(X\) 伪造一个能被正确解码的 \(Y'\neq\text{Ev}(F,X)\)。
关于这三种安全概念的测试的定义如下图
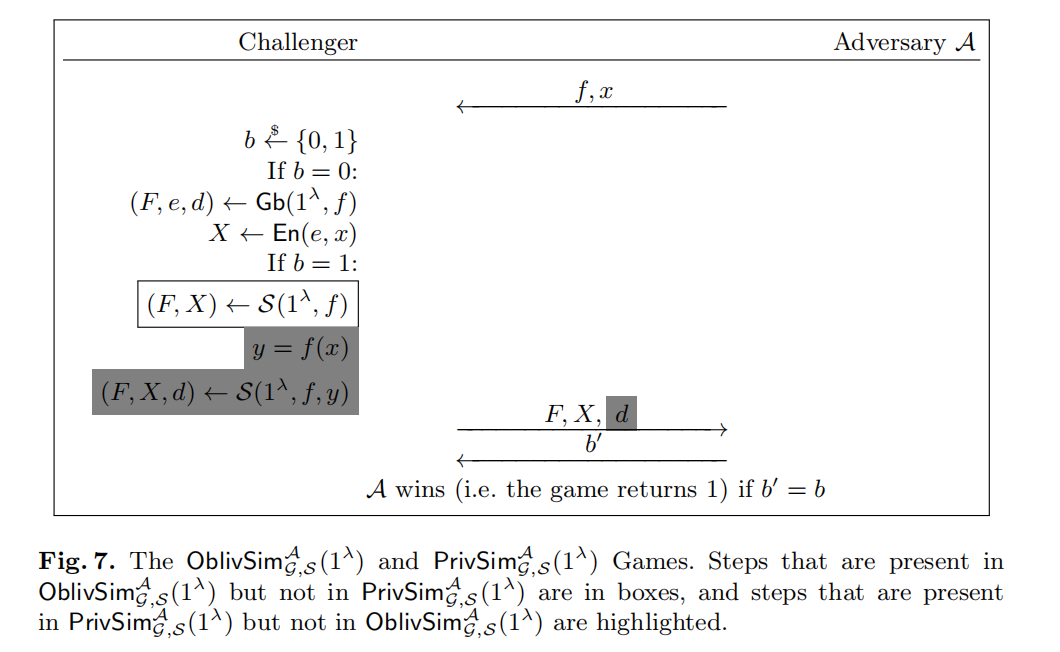
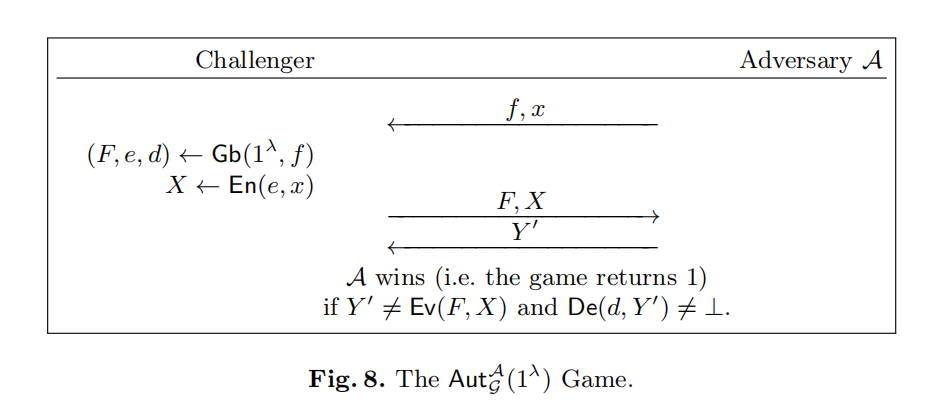
Oblivious Transfer
参考资料:A Pragmatic Introduction to Secure Multi-Party Computation
简单地说,在 1-out-of-2 OT 协议中,Sender \(\mathcal S\) 有一个秘密比特串 \(x_0,x_1\in\{0,1\}^n\),Receiver \(\mathcal R\) 选择一个比特 \(b\in\{0,1\}\),\(\mathcal R\) 在不向 \(\mathcal S\) 暴露 \(b\) 的值的同时,得到 \(x_b\) 的值,且 \(\mathcal S\) 不暴露 \(x_{\lnot b}\) 的值。
Circuit PSI
简而言之,Yao’s Garbled Circuits 提供了一种计算任意逻辑电路 \(C\) 的安全协议。因此,我们只需要构造这个逻辑电路。